
How modular design will enable blockchains to scale by orders of magnitude.
模块化设计如何赋能区块链按订单量级扩展
模块化区块链范式 (The Modular Blockchain Paradigm)
Modular blockchains are the latest paradigm in blockchain design. Originated by Celestia, the concept of modularity is rapidly becoming a category-defining narrative when it comes to the challenge of scaling blockchains by orders of magnitude.
模块化区块链是区块链设计的最新范式。由 Celestia 发起,当涉及到将区块链按数量级扩展的挑战时,模块化的概念正在迅速成为一种类别定义的描述。
But why do we need modular blockchains? Consider the following four theses:
但为什么我们需要模块化区块链?考虑以下四个论点:

上图翻译:
1.增加吞吐量是我们实现Web3愿景的必经之路
2.去中心化是我们实现Web3愿景的必经之路
3.增加了吞吐量却牺牲了去中心化,那就不是扩容
4.当前的单篇L1和L2扩展解决方案不足以实现真正的扩展
Based on these principles, it becomes clear that we need to look to new paradigms in order to achieve our vision for web3. Modular blockchains are the most promising new paradigm.
基于这些原则,很明显我们需要寻找新的范式,来实现我们对 web3 的愿景。模块化区块链是最有前途的新范式。
什么是模块化区块链 (What is a Modular Blockchain?)
Before diving deeper into the four statements above, it is important to understand the basics of monolithic and modular blockchains.
在深入研究上述四个陈述之前,了解单片和模块化区块链的基础知识非常重要。
The core functions of a blockchain are:
区块链的核心功能是:
-
Execution - Transaction processing and computation.
执行 - 事务处理和计算。 -
Settlement - Dispute resolution and bridging.
清算 - 争议解决和跨链。 -
Consensus - Transaction ordering.
共识 - 交易排序 -
Data availability - Ensures data is available.
数据可用性 - 确保数据可用
Traditionally, blockchain designs have been monolithic. This means that all the functions of the blockchain are handled on a single layer.
传统上,区块链设计一直是 单片。这意味着区块链的所有功能都在单层维度上处理。
The thesis of modular blockchains is that a single blockchain doesn’t need to handle all these components on its own. Instead, by disaggregating these core components, individual blockchains can focus on specializing in a specific area, leading to significant optimizations.
模块化 区块链的论点是单个区块链不需要自己处理所有这些组件。相反,通过分解这些核心组件,单个区块链可以专注于特定领域,从而实现显着优化。
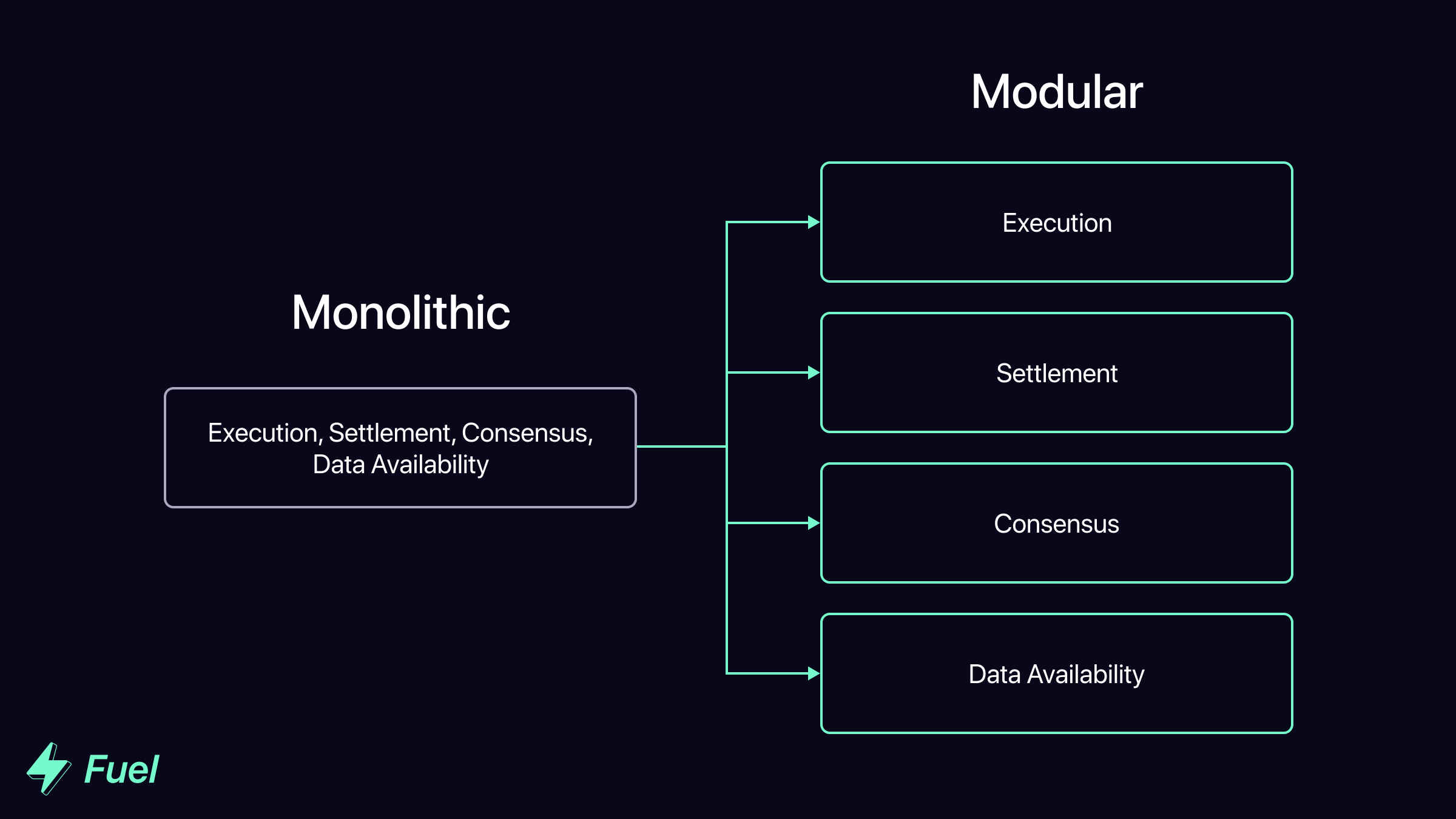
单片 vs. 模块化区块链堆栈(原图来源) Monolithic vs. modular blockchain stack (original image source)
A modular blockchain stack consists of layers of modular blockchains which rely on each other to create a system with all of the above components. A modular blockchain is any chain which is part of a modular blockchain stack.
模块化区块链技术栈由多层模块化区块链组成,它们相互依赖以创建具有所有上述组件的系统。模块化区块链是作为模块化区块链技术栈一部分的任何链。
Modular blockchain (noun): a blockchain that fully outsources at least one component to an external chain:
- Execution
- Settlement
- Consensus
- Data availability
— Celestia (@CelestiaOrg) June 27, 2022
模块化区块链(名词):将至少一个组件完全外包给外部链的区块链:
- 执行
- 结算
- 共识
- 数据可用性
— Celestia (@CelestiaOrg) 2022 年 6 月 27 日
为什么要模块化? (Why Modular?)
Fundamentally, blockchains are designed to protect and promote the sovereignty of the individual. Our vision for web3 is a world where the systems that form the fabric of our digital world are accessible by everyone, and are decentralized, scalable, and secure.
从根本上说,区块链旨在保护和促进个人的主权。 我们对 web3 的愿景是一个这样的世界:在这个世界中,构成我们数字世界结构的系统可供所有人访问,并且是去中心化的、可扩展的和安全的。
Above, we considered four statements which justify the development of a new paradigm for blockchains - specifically, the modular paradigm. Let's explore these further.
上面,我们考虑了四个开发区块链新范式的陈述——特别是模块化范式。让我们进一步探讨这些。
1 - 提高吞吐量对于实现我们的 Web3 愿景至关重要 (1 - Increased Throughput is Essential In Order to Achieve our Vision for Web3)
Despite the expansive ecosystem of existing blockchains, demand still far outstrips supply when it comes to throughput. This leads to network congestion, making blockchain networks increasingly inaccessible for many potential users.
尽管现有区块链的生态系统很广阔,但在吞吐量方面,需求仍然远远超过供应。这导致网络拥塞,使许多潜在用户越来越无法访问区块链网络。
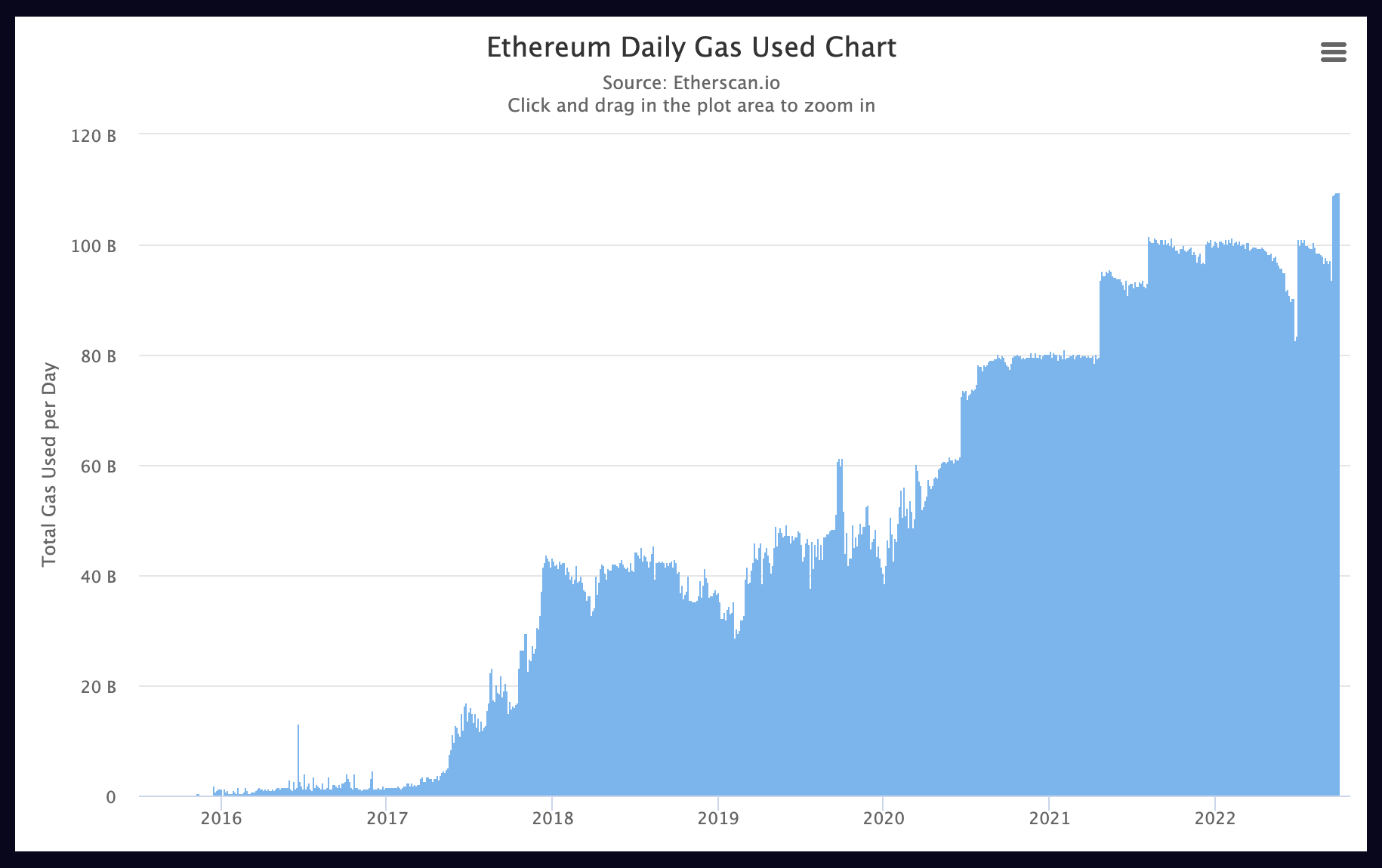
像以太坊这样的网络变得越来越拥挤(来源: Etherscan) Networks like Ethereum are becoming increasingly congested (source: Etherscan)
This challenge has plagued the blockchain space since its inception, even though adoption is still relatively low. Without new technologies to increase throughput, it will only become more of a problem as adoption scales to the billions.
这一挑战自诞生以来就一直困扰着区块链领域,尽管区块链采用率仍然相对较低。如果没有新技术来提高吞吐量,随着采用规模扩大到数十亿,它只会成为一个更大的问题。
To achieve our vision of making web3 systems accessible by everyone, they need to be able to scale accordingly. Mass adoption requires a massive increase in transactional and computational throughput.
为了实现我们让每个人都可以访问 web3 系统的愿景,他们需要能够相应地扩展。 大规模采用需要大量增加事务和计算吞吐量。
2 - 为了实现我们对 Web3 的愿景,去中心化是必需的 (2 - Decentralization is Essential In Order to Achieve our Vision for Web3)
Decentralization is the key differentiator between web2 and web3 systems, and as such should be the core focus of any web3 system. Without decentralization, web3 systems are no better than their web2 predecessors.
去中心化是 web2 和 web3 系统之间的关键区别,因此也会是任何 web3 系统的核心焦点。如果没有去中心化,web3 系统并不比它们的 web2 前辈更好。
The following principles are essential to achieving decentralization:
以下原则对于实现去中心化至关重要:
-
Openness - Anyone can view and access the system.
开放性 - 任何人都可以查看和访问系统。 -
Verifiability - Anyone can verify the validity of the system. Any user can operate a node and guarantee that the blockchain is operating correctly and that its rules are being upheld by validators.
可验证性 - 任何人都可以验证系统的有效/合法性。任何用户都可以操作一个节点并保证区块链正确运行并且其规则得到验证者的支持。 -
Censorship resistance - Anyone can participate in the system as a user without the risk of being locked out by validators.
抗审查性 - 任何人都可以作为用户参与系统,而不会有被验证者锁定的风险。
Thus, in order to achieve our vision for web3, any blockchain system must guarantee openness, verifiability, and censorship resistance - and all at a scale that can service billions of users.
因此,为了实现我们对 web3 的愿景,任何区块链系统都必须保证开放性、可验证性和抗审查性——并且所有这些都必须具备能够为数十亿用户提供服务的规模。
3 - 增加吞吐量却不保持去中心化,就不是真正的可扩展性 (3 - Increasing Throughput Without Maintaining Decentralization is Not Scaling)
The now-notorious Blockchain Scalability Trilemma describes the compromise monolithic blockchains must make between security, throughput, and decentralization. In order to improve one of these three components, sacrifices must be made in one or more of the others.
现在臭名昭著的区块链可扩展性三难困境描述了单片区块链必须在 安全、吞吐量 和 去中心化 之间做出妥协.为了改进这三个组成部分中的一个,必须在其他一个或多个方面做出牺牲。
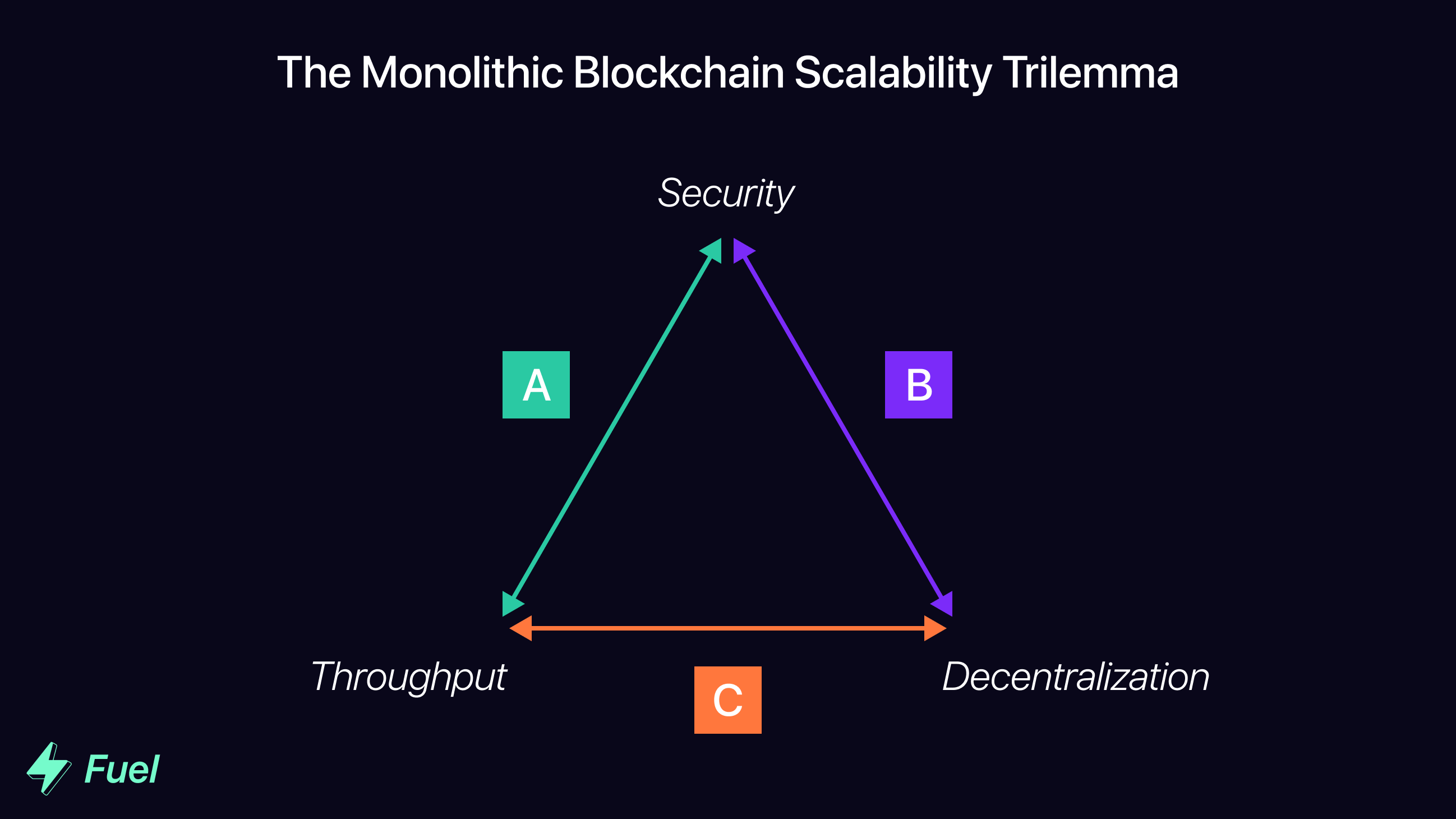
大多数单片区块链将自己定位在 A、B 或 C 组中,从而牺牲了三个核心方面之一 Most monolithic blockchains position themselves in group A, B, or C, thereby sacrificing one of the three core facets
Plenty of existing blockchains promise high throughput. However, in order to achieve this, they often make unacceptable sacrifices when it comes to decentralization.
大量现有的区块链承诺高吞吐量。然而,为了实现这一点,他们在去中心化方面经常做出不可接受的牺牲。
In today’s monolithic blockchain systems, increased throughput is correlated with an increased cost to verify the chain. As blocks become larger or more frequent, the resource requirements for verifying the validity of a block and/or blockchain increase. As such, fewer users are able to verify the chain, instead having to rely on an increasingly centralized group of trusted third parties to run nodes.
在当今的单片区块链系统中,增加的吞吐量与增加的验证成本相关。随着区块变得更大或更频繁,验证区块和/或区块链有效性的资源需求增加。因此,能够验证链的用户更少,而不得不依赖越来越集中的可信第三方来运行节点。
It is important to note: sacrificing decentralization to increase throughput is not scaling.
重要的是要注意:牺牲去中心化来增加吞吐量不是扩展。
While the term “scalability” has often been used to refer to a blockchain’s capacity to process transactions, there is a movement to redefine scalability as a blockchain’s throughput divided by the cost to verify the chain.
虽然“可扩展性”一词经常被用来指代区块链处理交易的能力,但有一种趋势是重新定义可扩展性为 区块链的吞吐量除以验证链的成本。

“可扩展性”可以定义为区块链的吞吐量除以验证所有交易的成本(来源:Celestia) “Scalability” can be defined as a blockchain’s throughput divided by the cost to validate all transactions (source: Celestia)
Under this definition, in order to scale, blockchains must increase throughput without increasing the cost to verify the network. This kind of “true scalability” is what modular blockchains are designed to enable.
根据这个定义,为了扩展,区块链必须在不增加验证网络成本的情况下增加吞吐量。这种“真正的可扩展性”是模块化区块链旨在实现的。
4 - 当前的单片 L1 和 L2 扩展解决方案不足以实现真正的可扩展性 (4 - Current Monolithic L1 and L2 Scaling Solutions are Not Sufficient to Achieve True Scalability)
There are many proposed scaling solutions for monolithic blockchains, some of which are already under development. Solutions like sharding, rollups, fraud/validity proofs, and light client innovations aim to increase throughput without increasing the cost to verify the network.
有许多针对单片区块链的扩展解决方案,其中一些已经在开发中, sharding、rollups、fraud/有效性证明和轻客户端创新,都旨在增加吞吐量而不增加验证网络的成本。
Some of these solutions are adopting aspects of modularity in order to scale, such as outsourcing execution to L2s. However, L2s are severely restricted by the performance of the main network, so as long as they continue to rely on monolithic L1s for finality, the scalability trilemma remains an issue.
其中一些解决方案正在采用模块化方面来实现扩展,例如将执行外包给 L2。然而,L2s 受到主网性能的严重限制,因此只要它们继续依赖单片 L1s 来实现最终性,可扩展性三难困境仍然是一个问题。
For example, rollups on Ethereum post their blocks directly to the Ethereum blockchain, essentially using L1 Ethereum as a settlement, consensus, and data availability layer. The problem with this is that Ethereum is already congested, and rollups are competing for bandwidth with users of “monolithic Ethereum” (i.e. non-rollup use cases).
例如,以太坊上的汇总将其块直接发布到以太坊区块链,本质上使用 L1 以太坊作为结算、共识和数据可用性层。这样做的问题是以太坊已经拥塞,并且汇总正在与“单片以太坊”(即非汇总用例)的用户竞争带宽。
Because of their growing popularity, rollups are causing further congestion on Ethereum, thereby inadvertently driving Ethereum toward a more modular-first design. For example, there are already several proposals to make gas costs cheaper for rollups on Ethereum (i.e. prioritizing modularity), but this move is controversial, as it will make typical Ethereum transactions more expensive, essentially forcing users of L1 Ethereum to subsidize rollups.
由于它们越来越受欢迎,汇总正在导致以太坊进一步拥塞,从而无意中将以太坊推向更加模块化优先的设计。例如,已经有 几个 提案 来降低以太坊上汇总的 gas 成本(即优先考虑模块化),但这一举措是有争议的,因为它将使典型的以太坊交易更加昂贵,实质上迫使L1以太坊的用户补贴汇总。
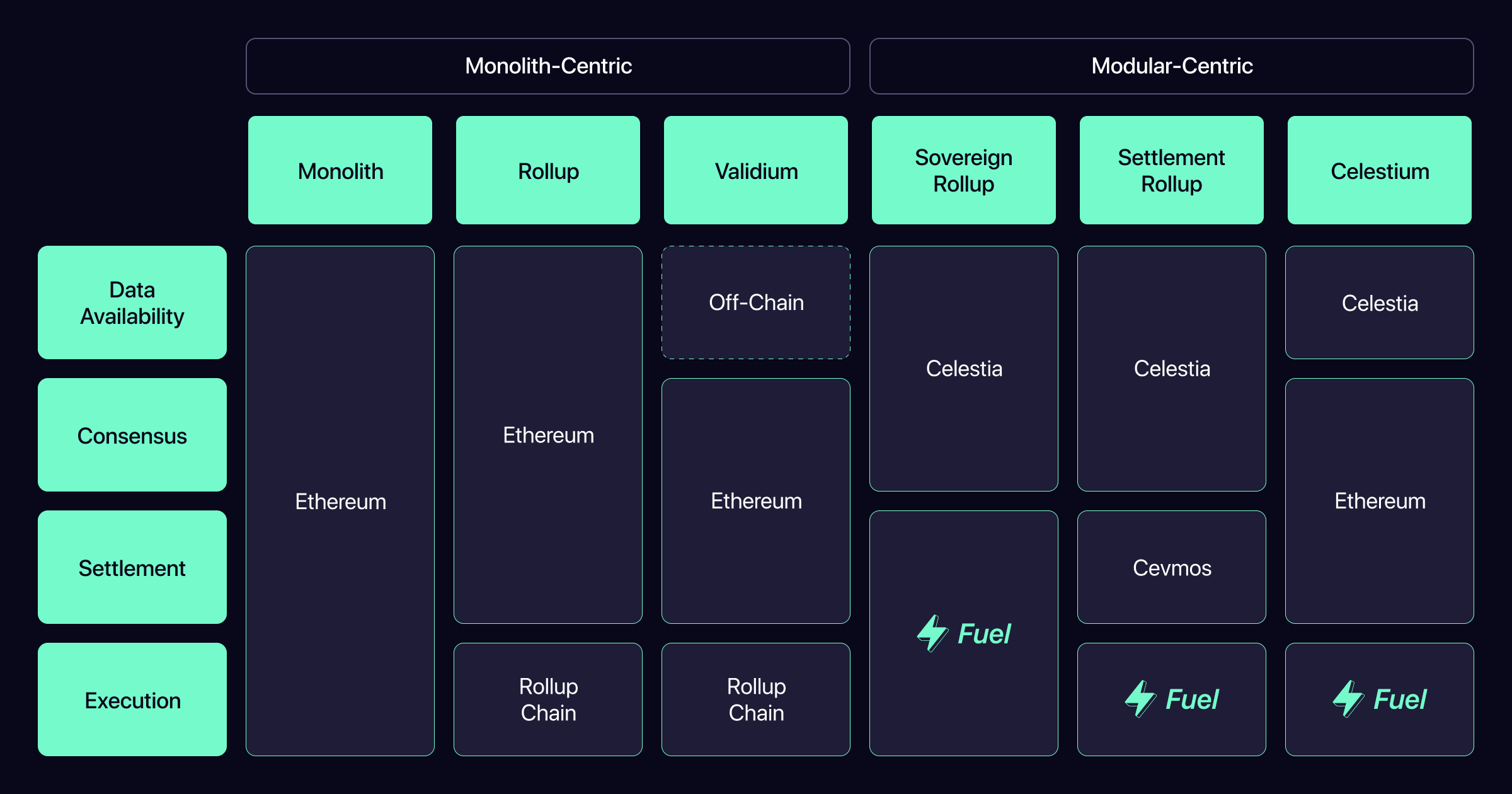
在以太坊之上的汇总必须与整体以太坊的非汇总用例竞争空间,这是模块化优先区块链避免的问题([原始图像源](https://twitter.com/ptrwtts/status/ 1509869606906650626)) Rollups on top of Ethereum have to compete for space with non-rollup use cases of monolithic Ethereum, a problem which is avoided by modular-first blockchains (original image source)
This conflict between modular and monolithic use cases of Ethereum means it is failing to effectively optimize for modularity. As long as it remains unspecialized, it will have reduced scale compared to modular-first alternatives.
以太坊的模块化和单片用例之间的冲突意味着它未能有效地优化模块化。只要它保持非专业化,与模块化优先的替代方案相比,它的容量就会减少。
True scalability - that is, massively increased throughput which preserves decentralization - is not a viable goal for monolithic blockchains. In order to scale, chains like Ethereum will need to optimize for modularity, which will mean outsourcing execution entirely.
真正的可扩展性 - 即在保持去中心化的情况下大幅增加吞吐量 - 对于单片区块链来说不是一个可行的目标。 为了扩展,像以太坊这样的链需要针对模块化进行优化,这意味着完全外包执行。
模块化区块链的承诺 (The Promise of Modular Blockchains)
Novel modular blockchain systems are designed from the ground up to solve barriers to scalability. Rather than building on top of dated technology, the aim is to learn from the suboptimal elements of previous generations of blockchain tech and create an entirely new paradigm which optimizes for scalability and decentralization while maintaining security.
全新的模块化区块链系统是从头开始设计的,进而来解决可扩展性的障碍。其目标不是建立在过时的技术之上,而是从前几代区块链技术的次优元素中学习,并创建一个全新的范式,在保持安全性的同时优化可扩展性和去中心化。
In a modular system, protocols can specialize their offering for a specific layer in the stack. With teams like Celestia working on a dedicated data availability and consensus layer, there is a new drive for projects which optimize for solving bottlenecks on the execution layer. Fuel is tackling this challenge by building the world’s fastest execution layer for the modular stack.
在模块化系统中,协议可以专门针对堆栈中的特定层提供定制服务。随着像 Celestia 这样的团队致力于专门的数据可用性和共识层,对于优化解决执行层瓶颈的项目有了新的驱动力。 Fuel 正在通过构建世界上最快的模块化堆栈执行层来应对这一挑战。
Unconstrained by the limitations of Ethereum and the EVM, Fuel approaches scalable execution from a modular-first perspective, allowing for significant improvements over the EVM’s inefficient execution environment and thus enabling maximum decentralization and the highest flexible throughput.
不受以太坊和 EVM 的限制,Fuel 从模块化优先的角度实现可扩展的执行,允许 [对 EVM的低效执行环境进行重大改进](https://fuellabs.github.io/fuel-docs/master/vs-evm .html) ,从而实现最大程度的去中心化和最大的灵活吞吐量。
With this new movement, we have an opportunity to start fresh and build a fundamentally new generation of blockchains that go beyond monolithic.
借助这一新运动,我们有机会重新开始并构建从根本上超越单片**的新一代区块链。
敬请关注 (Follow Us)
关于我们 (About Us)
Fuel is the fastest execution layer for the modular blockchain stack. Powerful and sleek, the technology enables parallel transaction execution, empowering developers with the highest flexible throughput and maximum security required to scale. Developers choose the FuelVM for its superior developer experience and the ability to go beyond the limitations of the EVM.
Fuel 是模块化区块链堆栈的最快执行层。该技术功能强大且时尚,支持并行交易执行,为开发人员提供了扩展所需的最高灵活吞吐量和最大安全性。开发人员选择 FuelVM 是因为它卓越的开发人员体验和运行能力 ,突破了 EVM 的限制****。

